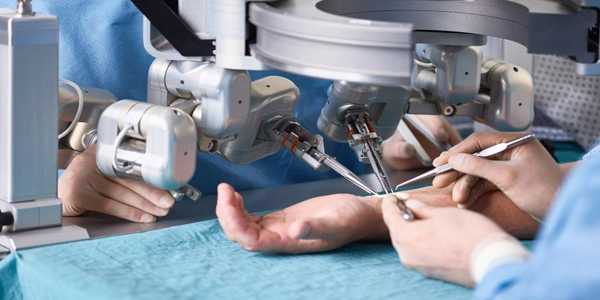
Robotic Surgery: Transforming Medicine with Precision and Innovation
 Health & medical treatment
Health & medical treatment Robotic surgery has become one of the most transformative developments in modern medicine. Over the past few decades, it has reshaped how surgeries are performed, offering a blend of precision, flexibility, and minimal invasiveness. From its early beginnings to its current state, robotic surgery has been marked by significant technological advancements, expanding applications, and ongoing innovation. As we approach 2025, these systems are increasingly sophisticated, promising even more substantial improvements in surgical care, patient outcomes, and the overall healthcare experience.
Robotic surgery has become one of the most transformative developments in modern medicine. Over the past few decades, it has reshaped how surgeries are performed, offering a blend of precision, flexibility, and minimal invasiveness. From its early beginnings to its current state, robotic surgery has been marked by significant technological advancements, expanding applications, and ongoing innovation. As we approach 2025, these systems are increasingly sophisticated, promising even more substantial improvements in surgical care, patient outcomes, and the overall healthcare experience.
Early Beginnings: The Genesis Of Robotic Surgery
The roots of robotic surgery date back to the 1980s, when the idea of using robotics in medicine was first explored. The concept was not entirely new; human fascination with machines that could mimic human movements stretches back centuries. Visionaries like Leonardo da Vinci designed automata in the 15th century, but in the 20th century, such ideas began to be realized through advanced engineering and computing.
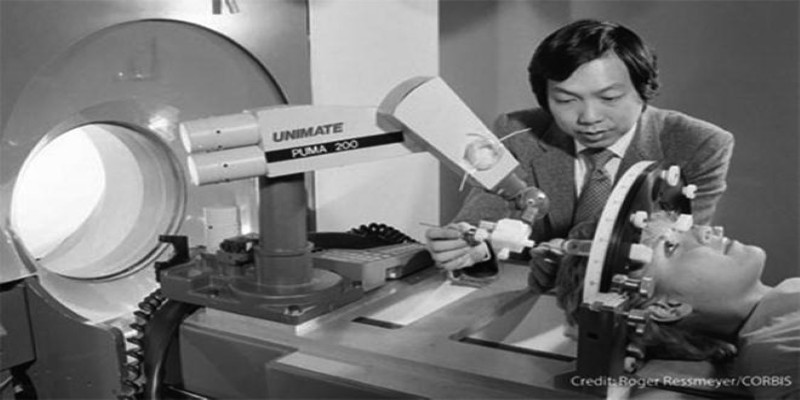

In 1985, the first robotic-assisted surgery was performed. Known as the "PUMA 560," it was a system designed to assist in brain surgery. However, it was not until 2000, with the introduction of the da Vinci Surgical System, that robotic surgery gained widespread attention. This system allowed surgeons to perform minimally invasive surgeries with greater precision than ever before, setting the stage for the future of robotic-assisted procedures.
The da Vinci system marked a significant turning point in the field, offering robotic arms that could perform delicate movements with far greater control than the human hand. Surgeons could now manipulate instruments via a console, viewing the surgical site in 3D with magnified visuals. These early systems were bulky, expensive, and limited in their capabilities, but they demonstrated the potential for improving surgical outcomes, reducing complications, and shortening recovery times.
Expansion And Improvement: The Growth Of Robotic Surgery
As the 2000s progressed, so did the capabilities of robotic surgical systems. Over time, the systems became more compact, sophisticated, and versatile. By the mid-2010s, robotic surgery was no longer limited to just a few specialized procedures. It expanded into various fields, including general surgery, urology, gynaecology, and cardiac surgery.
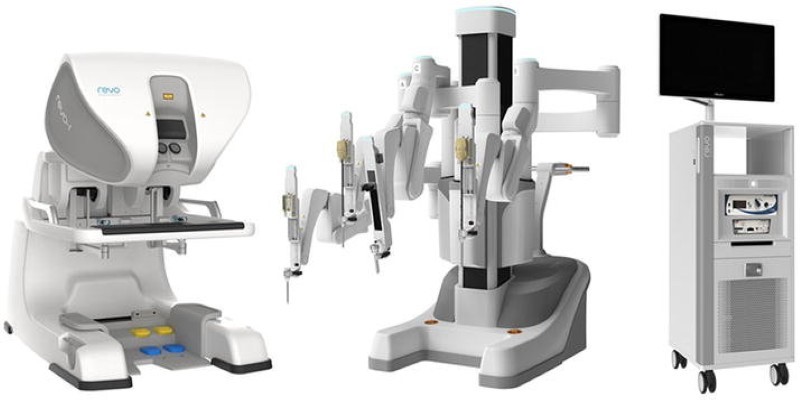
One key driver behind this growth was the refinement of robotic systems to make them more accessible and cost-effective. New platforms emerged, offering advanced features that could rival or surpass the da Vinci system in precision, flexibility, and ease of use. Systems like the Senhance, Revo-I, and Versius have gained traction, each bringing innovations such as haptic feedback, enhanced dexterity, and improved ergonomics.
In recent years, robotic systems have become smaller, lighter, and more capable of performing complex tasks. One breakthrough was the ability to perform remote robotic surgeries, with surgeons operating robotic systems from thousands of miles away. This capability proved invaluable during the COVID-19 pandemic, allowing specialists to perform critical surgeries while minimizing direct contact, thus reducing the risk of transmission.
Advancements In Technology: Artificial Intelligence And Automation
The next frontier in robotic surgery is integrating artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML). These technologies have been increasingly incorporated into robotic systems to enhance surgical precision and decision-making. AI can analyze real-time data, provide predictive insights, and even suggest optimal surgical strategies. Surgeons can rely on AI to reduce human error, improve efficiency, and customize treatment plans to suit individual patients' needs.

One example of this integration is the application of AI to improve navigational capabilities. AI algorithms can analyze medical imaging and assist surgeons in planning the most efficient and least invasive surgical paths. Furthermore, AI can adapt to new data during a procedure, adjusting the robot’s actions based on live feedback.
AI is also paving the way for more autonomous surgical procedures. While we are not yet at the point where robots can perform entire surgeries independently, ongoing research in AI-driven robotics explores partial autonomy. This could include robots capable of executing standard procedures, such as suturing or tissue removal, without direct human intervention.
Minimally Invasive Surgery And Patient Benefits
One of the key advantages of robotic surgery has always been its minimally invasive nature. Unlike traditional open surgeries, which involve large incisions, robotic-assisted surgeries can often be performed through small incisions, reducing the trauma to the body. This results in less pain, faster recovery times, and fewer complications like infections. This translates to a quicker return to daily activities and a significantly improved overall experience for patients.
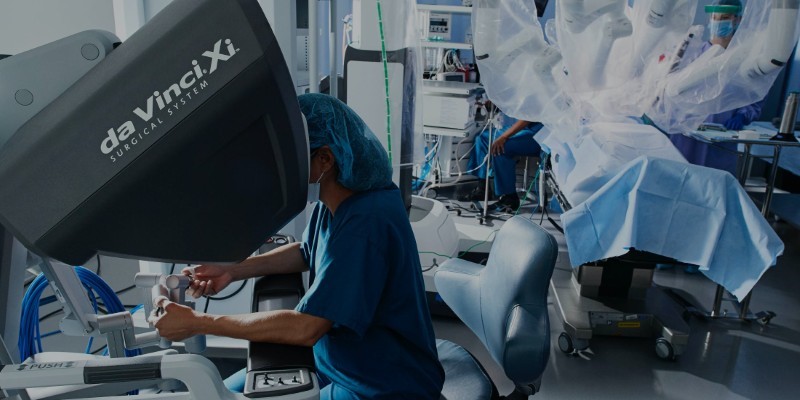
The da Vinci Surgical System, for example, is widely used in prostate cancer surgery. It allows for the precise tumour removal with minimal impact on surrounding tissues. This precision reduces the risk of complications such as nerve damage, leading to better long-term outcomes. Similarly, in gynaecology, robotic surgery is frequently used for procedures like hysterectomies and fibroid removals, offering faster healing and reduced scarring.
As robotic surgery becomes more advanced, even more complex procedures are being tackled with this technology. In the future, robots will likely be capable of performing surgeries in highly delicate areas, such as the brain or heart, where the need for precision is paramount. Enhanced visualization and dexterous robotic arms enable surgeons to perform tasks with a level of accuracy previously unattainable.
The Role Of Teleoperation And Remote Surgery
Another significant development in robotic surgery is teleoperation, which allows surgeons to perform procedures remotely. This capability has vast potential, especially for patients in underserved or remote areas who might not otherwise have access to specialized care. Surgeons can operate robotic systems in hospitals worldwide, performing procedures as if they were right there in the operating room.
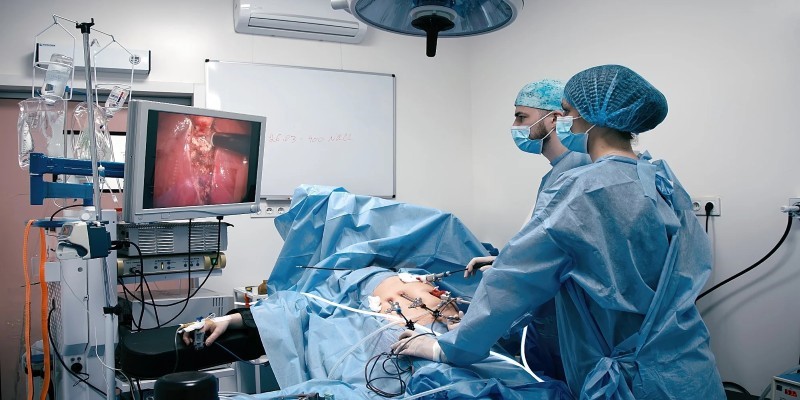
The COVID-19 pandemic accelerated the adoption of telesurgery, demonstrating its potential in critical situations where in-person visits were not feasible. Remote surgery has expanded beyond emergencies, offering a new avenue for global collaboration and access to world-class expertise.
Conclusion
The journey of robotic surgery is one of innovation and progress. The field has evolved tremendously from its early days with the da Vinci Surgical System to the latest AI-driven platforms. In 2025, robotic surgery promises to improve the precision, safety, and accessibility of medical procedures, offering hope for even more breakthroughs in the future. As technology continues to evolve, so will the role of robots in the operating room, reshaping medicine as we know it.
